Do you know why Hackers Fear TLS? Today, I shall show you the Secret Behind Secure Browsing in just 10 Minutes.
Ever noticed the little padlock icon next to a website's address in your browser? That tiny symbol is doing something huge- it's protecting your data from hackers, spies, and digital eavesdroppers. Behind that lock lies one of the most powerful shields in cybersecurity: Transport Layer Security, or TLS.
Let's break it down. Imagine sending a secret letter to your bestie. If you hand it to someone you don't trust, they could read it. But if you seal it in an unbreakable envelope, no one can peek inside. That's what TLS does- it seals your internet communication in a digital envelope.
And the best part? You don't have to be a coding genius to understand how it works. By the end of this tutorial, you'll know exactly what TLS is, how it works, and why it matters — even if you're just starting your cybersecurity journey.
What is TLS?
TLS (Transport Layer Security) is a cryptographic protocol that keeps your internet data safe. It ensures that the information you send or receive can't be read, changed, or faked during transit.
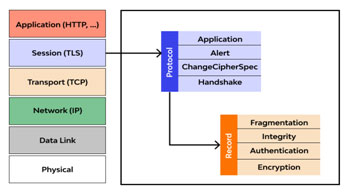 You've already used TLS today; maybe while checking your email, logging into a website, or making a payment online. TLS is working silently in the background, making sure your messages, passwords, and credit card numbers are only seen by the person or system they're meant for.
You've already used TLS today; maybe while checking your email, logging into a website, or making a payment online. TLS is working silently in the background, making sure your messages, passwords, and credit card numbers are only seen by the person or system they're meant for.
TLS is the successor of SSL (Secure Sockets Layer- Handshake protocol). Though people still say "SSL," modern systems actually use TLS. It is used by HTTP, SMTP.
Why is TLS so Important?
Let's say you're using public Wi-Fi at a café. Without TLS, anyone on that network could spy on what you're typing — your Facebook login, your bank info, even your private messages.
TLS protects you from:
- Man-in-the-middle attacks (when a hacker sits between you and a website to steal your data)
- Data tampering
- Identity theft
It gives you three layers of security:
- Encryption – No one can read your data.
- Integrity – Your data can't be secretly changed.
- Authentication – You're sure you're talking to the real website, not a fake one.
How Does TLS Actually Work?
It uses a client-server handshake mechanism.
- Key exchange between client and server (It may happen by Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange Algorithm)
- Now TLS protocol will open an encryption channel (by RCA/IDEA/DES Algorithm)
- It also ensures that the messages are not altered. (by MD5/ SHA Algorithm)
Let's explain TLS in a human way.
 Say, you walk into a secret club. At the door, the guard (your browser) asks the club owner (the website) for an ID (a certificate). The owner shows a certificate signed by a trusted organization (like DigiCert or Let's Encrypt). If it checks out, the guard lets you in safely.
Say, you walk into a secret club. At the door, the guard (your browser) asks the club owner (the website) for an ID (a certificate). The owner shows a certificate signed by a trusted organization (like DigiCert or Let's Encrypt). If it checks out, the guard lets you in safely.
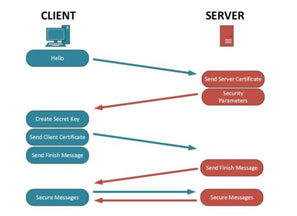
That's how TLS Handshake works:
- Hello! – Your browser says "Hi" to the server and asks for a secure connection.
- Certificate Check – The server sends its digital certificate to prove it's trustworthy.
- Key Exchange – They agree on secret keys to use for this session.
- Secure Channel – Now they talk using encryption, so no one else can listen in.
All of this happens in milliseconds. Amazing, right?
What is a TLS Certificate?
Think of it like a digital passport for a website. It contains:
- The domain name
- The organization behind it
- The certificate authority that issued it
- An expiration date
- A public key (used for encryption)
Browsers trust certificates only if they're signed by a Certificate Authority (CA). This trust chain is what keeps you safe.
You can even view any website's certificate by clicking the padlock in your browser.
TLS Versions: What You Need to Know
TLS has had a few versions over the years:
- TLS 1.0 and 1.1 – Outdated. Do not use. Weak encryption.
- TLS 1.2 – Still widely used and very secure.
- TLS 1.3 – The newest, fastest, and most secure version.
If you're a student or developer, always aim to use TLS 1.2 or 1.3 in your apps and websites.
Real-Life Examples of TLS:
 When you buy something on Amazon, TLS ensures your card details aren't exposed.
When you buy something on Amazon, TLS ensures your card details aren't exposed.- Logging into Instagram? TLS makes sure your password isn't stolen on the way.
- Running a cybersecurity tool or sending commands to a server? TLS secures your terminal or API connections.
TLS is like the oxygen of secure communication — invisible but essential.
Who Needs to Understand TLS?
Everyone who uses the internet. Seriously.
But if you're:
- A cybersecurity student → It's foundational knowledge.
- A web developer → You must know how to implement it.
- An ethical hacker or pentester → You'll need to test if TLS is configured correctly.
- A general user → Knowing when a site is secure can protect you from scams.
How to Check if TLS is Working?
Easy steps:
- Look for HTTPS in the URL.
- Click the padlock → View connection details.
- Use SSL Labs (https://www.ssllabs.com/ssltest/) to test websites for TLS strength.
- As a dev, use tools like OpenSSL to inspect certificates and connections.
Common TLS Mistakes to Avoid:
- Using expired certificates
- Not redirecting HTTP to HTTPS
- Allowing outdated TLS versions
- Not renewing certificates in time
- Trusting self-signed certs in public environments
These mistakes make it easy for attackers to break into your connection.
How to Enable TLS on Your Website (in 2 Steps)?
- Get a certificate – From a trusted Certificate Authority (free via Let's Encrypt).
- Configure your server – Most web hosts offer "one-click" HTTPS setup.
And that's it! Your site will now speak in encrypted language.
Why You Should Care?
Every time you send a message, log in, or buy something online, TLS is your digital bodyguard. It's simple, powerful, and everywhere.
Learning TLS not only boosts your cybersecurity awareness but also gives you the confidence to build, test, and defend real-world systems.
So next time you see that padlock, smile - you now know the magic behind it.
Hacking Tools
Explore All Hacking Tools »
UFTP is an encrypted multicast file transfer program for secure, reliable & efficient transfer of files. It also helps in data distribution over a satellite link.
Read DetailsBreaking News
Breaking News Of Each Month »
The recent pandemic was unexpected and unknown to most part of the world. It has changed our life and we are slowly adapting to our new lifestyle. The risks associated with the new lifestyle, both personal & corporate, are unknown to most of us.
Read Details