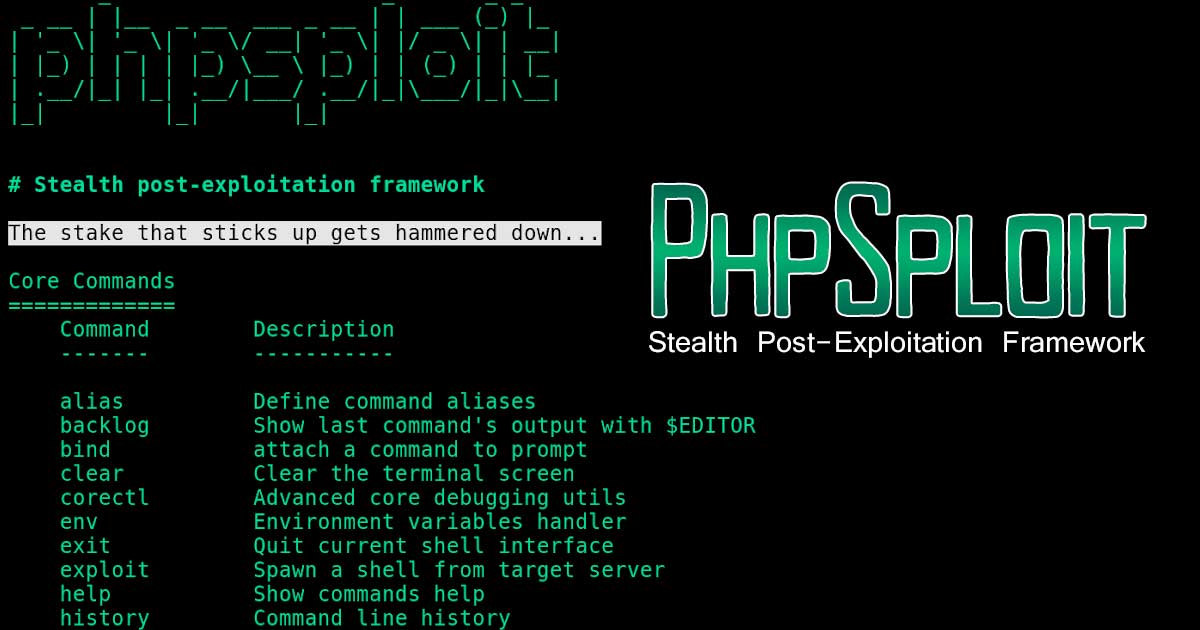
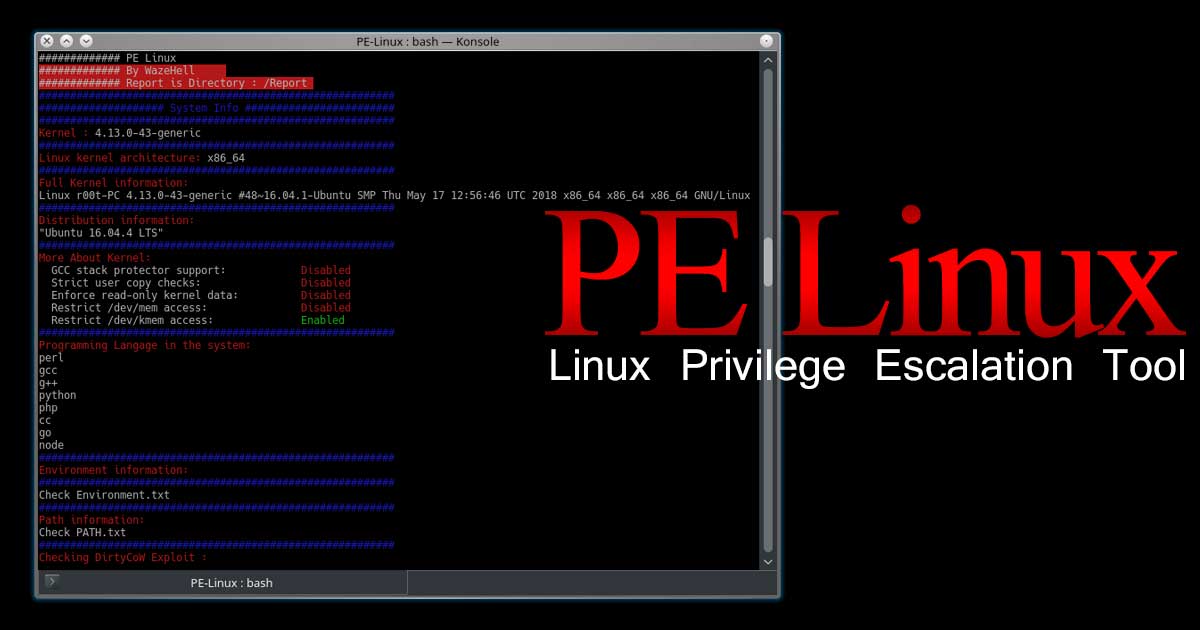
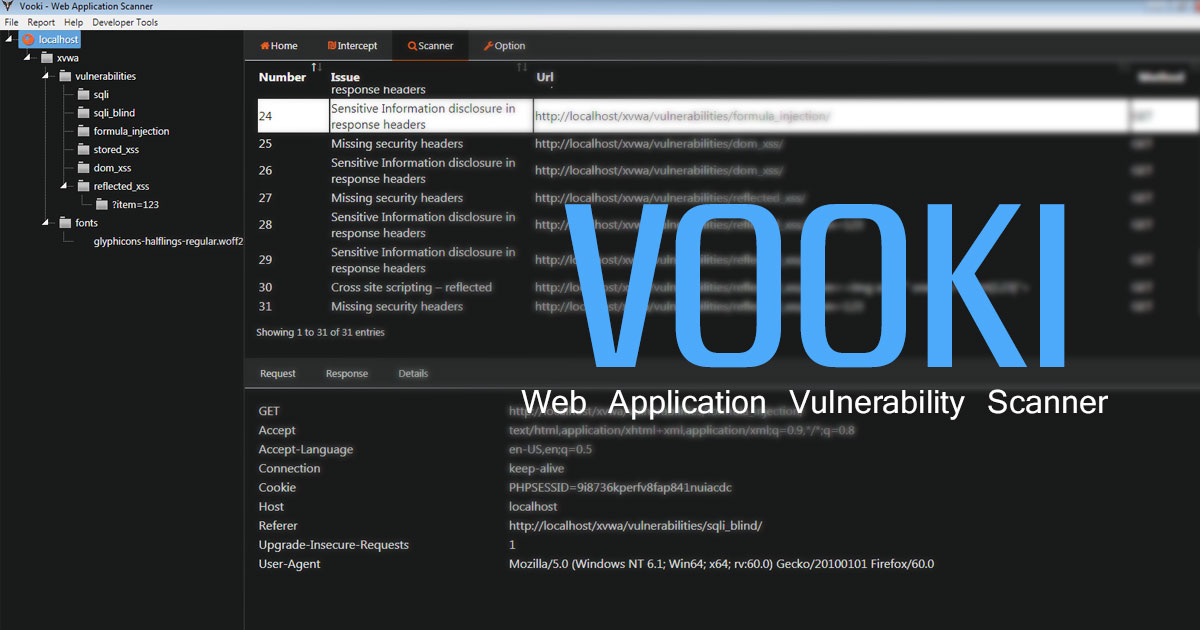
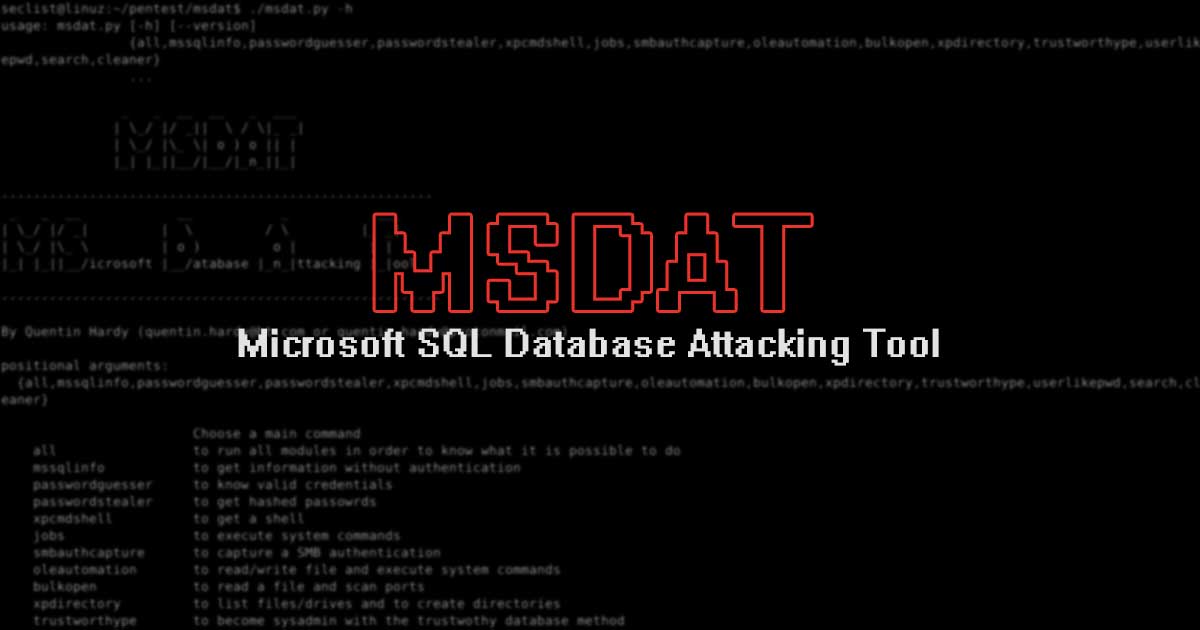
Qiling is an advanced binary emulation framework, with the following features:
- Cross platform: Windows, MacOS, Linux, BSD
- Cross architecture: X86, X86_64, Arm, Arm64, Mips
- Multiple file formats: PE, MachO, ELF
- Emulate & sandbox machine code in a isolated environment
- Provide high level API to setup & configure the sandbox
- Fine-grain instrumentation: allow hooks at various levels (instruction/basic-block/memory-access/exception/syscall/IO/etc)
- Allow dynamic hotpatch on-the-fly running code, including the loaded library
- True framework in Python, making it easy to build customized security analysis tools on top
Qiling is backed by Unicorn engine.
Visit our website https://www.qiling.io for more information.
License
This project is released and distributed under free software license GPLv2.
Qiling vs other Emulators
There are many open source emulators, but two projects closest to Qiling are Unicorn & Qemu usermode. This section explains the main differences of Qiling against them.
Qiling vs Unicorn engine
Built on top of Unicorn, but Qiling & Unicorn are two different animals.
- Unicorn is just a CPU emulator, so it focuses on emulating CPU instructions, that can understand emulator memory. Beyond that, Unicorn is not aware of higher level concepts, such as dynamic libraries, system calls, I/O handling or executable formats like PE, MachO or ELF. As a result, Unicorn can only emulate raw machine instructions, without Operating System (OS) context.
- Qiling is designed as a higher level framework, that leverages Unicorn to emulate CPU instructions, but can understand OS: it has executable format loaders (for PE, MachO & ELF at the moment), dynamic linkers (so we can load & relocate shared libraries), syscall & IO handlers. For this reason, Qiling can run executable binary without requiring its native OS.
Qiling vs Qemu usermode
Qemu usermode does similar thing to our emulator, that is to emulate whole executable binaries in cross-architecture way. However, Qiling offers some important differences against Qemu usermode.
- Qiling is a true analysis framework, that allows you to build your own dynamic analysis tools on top (in friendly Python language). Meanwhile, Qemu is just a tool, not a framework.
- Qiling can perform dynamic instrumentation, and can even hotpatch code at runtime. Qemu does not do either.
- Not only working cross-architecture, Qiling is also cross-platform, so for example you can run Linux ELF file on top of Windows. In contrast, Qemu usermode only run binary of the same OS, such as Linux ELF on Linux, due to the way it forwards syscall from emulated code to native OS.
- Qiling supports more platforms, including Windows, MacOS, Linux & BSD. Qemu usermode can only handles Linux & BSD.
Install
Run below command line to install Qiling (Python3 is required).
python3 setup.py install
Examples
- Below example shows how to use Qiling framework to emulate a Windows EXE on a Linux machine.
from qiling import *
# sandbox to emulate the EXE
def my_sandbox(path, rootfs):
# setup Qiling engine
ql = Qiling(path, rootfs)
# now emulate the EXE
ql.run()
if __name__ == "__main__":
# execute Windows EXE under our rootfs
my_sandbox(["examples/rootfs/x86_windows/bin/x86-windows-hello.exe"], "examples/rootfs/x86_windows")
- Below example shows how to use Qiling framework to dynamically patch a Windows crackme, make it always display "Congratulation" dialog.
from qiling import *
def force_call_dialog_func(ql):
# get DialogFunc address
lpDialogFunc = ql.unpack32(ql.mem_read(ql.sp - 0x8, 4))
# setup stack memory for DialogFunc
ql.stack_push(0)
ql.stack_push(1001)
ql.stack_push(273)
ql.stack_push(0)
ql.stack_push(0x0401018)
# force EIP to DialogFunc
ql.pc = lpDialogFunc
def my_sandbox(path, rootfs):
ql = Qiling(path, rootfs)
# NOP out some code
ql.patch(0x004010B5, b'\x90\x90')
ql.patch(0x004010CD, b'\x90\x90')
ql.patch(0x0040110B, b'\x90\x90')
ql.patch(0x00401112, b'\x90\x90')
# hook at an address with a callback
ql.hook_address(0x00401016, force_call_dialog_func)
ql.run()
if __name__ == "__main__":
my_sandbox(["rootfs/x86_windows/bin/Easy_CrackMe.exe"], "rootfs/x86_windows")
Qltool
Qiling also provides a friendly tool named qltool to quickly emulate shellcode & executable binaries.
To emulate a binary, run:
$ ./qltool run -f examples/rootfs/arm_linux/bin/arm32-hello --rootfs examples/rootfs/arm_linux/
To run shellcode, run:
$ ./qltool shellcode --os linux --arch x86 --asm -f examples/shellcodes/lin32_execve.asmDownload Tool: https://github.com/qilingframework/qiling
Exclusive Blog
Read All Exclusive Blog »
With world working from home, it's time to make it enjoyable and effective.
Read DetailsBreaking News
Breaking News Of Each Month »
The recent pandemic was unexpected and unknown to most part of the world. It has changed our life and we are slowly adapting to our new lifestyle. The risks associated with the new lifestyle, both personal & corporate, are unknown to most of us.
Read Details