Introduction
"Former Twitter CEO Jack Dorsey recently announced his vision for a new decentralized web platform that is being called Web 5.O and is being built, with an aim to return ownership of data and identity to individuals."
The deadliest web with an extra decentralized structure where individuals have control over their data and identity. Before introducing the new buzzword WEB 5.O, let’s have a quick explanation of Web 1.O, Web 2.O and Web 3.O.
The World Wide Web, which is the foundation of Web 1.0, was invented by British computer scientist Sir Tim Berners-Lee in 1989 while working at CERN, the European Organization for Nuclear Research. The first HTML website was launched in 1991.
The web is evolving too smartly.
Web 1.O
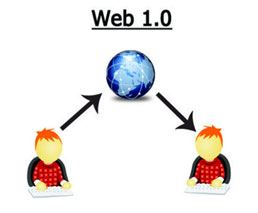 Web 1.0 emerged in the mid-1990s as the first generation of the World Wide Web. "Web 1.0 was read-only internet because it consisted of static pages that did not enable interaction."
Web 1.0 emerged in the mid-1990s as the first generation of the World Wide Web. "Web 1.0 was read-only internet because it consisted of static pages that did not enable interaction."
Mostly composed of basic text and graphics.
Web 1.0 websites were mainly designed for one-way communication, with the content being delivered from the website to the user, and there was limited interactivity and no user-generated content.
Characteristics:
- Static Content: Web 1.0 websites were primarily composed of static HTML pages with basic text and graphics.
- Limited Interactivity: Web 1.0 websites were mostly informational, with limited interactivity and no user-generated content.
- One-Way Communication: Web 1.0 websites were mostly designed for one-way communication, with the content being delivered from the website to the user.
- Limited Personalization: Web 1.0 websites did not offer personalized experiences, and content was not tailored to individual users.
- Limited Multimedia: Web 1.0 websites mostly used simple graphics and text, with little or no multimedia content.
- Limited Connectivity: Web 1.0 websites were not interconnected, and it was difficult to share information between different sites.
- Limited Functionality: Web 1.0 websites were mostly static and did not offer much in the way of interactive functionality or advanced features.
- Dial-Up Connections: Web 1.0 websites were designed for slow dial-up internet connections, with limited bandwidth and slower loading times.
Web 2.O
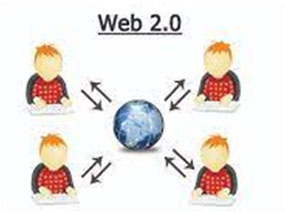 Web 2.0 refers to the second generation of the World Wide Web, which emerged in the early 2000s. It represents a shift towards more dynamic, interactive, and user-centric websites and applications. Mainly designed for two-way communication.
Web 2.0 refers to the second generation of the World Wide Web, which emerged in the early 2000s. It represents a shift towards more dynamic, interactive, and user-centric websites and applications. Mainly designed for two-way communication.
Characterized by user-generated content, social networking, collaboration, rich user experiences, web applications, openness, interoperability, personalization, and mobile support.
The term "Web 2.0" was first coined by Dale Dougherty of O'Reilly Media in 2004, and was later popularized by Tim O'Reilly and John Battelle.
While there is no specific person or organization that can be credited with inventing Web 2.0, it is generally considered to be a collaborative effort by developers, designers, and entrepreneurs who sought to improve the functionality and usability of the World Wide Web.
Some of the key players in the development of Web 2.0 include companies like Google, Facebook, Twitter, and YouTube.
Characteristics:
- User-Generated Content: Users are encouraged to contribute content, such as text, photos, and videos, and share it with others.
- Social Networking: Web 2.0 websites encourage social interaction and provide users with the ability to connect and share with others.
- Collaboration: Web 2.0 platforms allow users to collaborate and work together on projects and content creation.
- Rich User Experiences: Web 2.0 websites often feature multimedia content, such as video and audio, and use dynamic interfaces to provide a more engaging user experience.
- Web Applications: Web 2.0 platforms often feature web applications, such as online office suites, project management tools, and social media tools.
- Openness: Web 2.0 platforms often use open standards, such as RSS and XML, to enable sharing and interoperability between different applications and services.
- Interoperability: Web 2.0 platforms often integrate with other services and applications, such as social media sites, through APIs and other technologies.
- Personalization: Web 2.0 platforms often allow users to personalize their experience, such as through customizable profiles and content recommendations.
- Mobile support: Web 2.0 platforms are designed to work on mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets, to allow users to access content and services on the go.
Web 3.O
Web 3.0 is a term that is still evolving and has different meanings to different people.

Characteristics:
- Artificial Intelligence: Web 3.0 will be characterized by the extensive use of artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies that will enable websites and applications to learn and adapt to user behaviour.
- Semantic Web: Web 3.0 will enable more intelligent and sophisticated search capabilities, with a focus on making data more easily understandable and accessible to both humans and machines.
- Decentralization: Web 3.0 will move away from centralized control and instead focus on distributed systems and blockchain technology.
- Personalization: Web 3.0 will enable more personalized experiences by leveraging data and analytics to tailor content and services to individual users.
- Immersive Interfaces: Web 3.0 will be characterized by the use of immersive interfaces, such as virtual and augmented reality, that will enable more interactive and engaging user experiences.
- Interoperability: Web 3.0 will enable greater interoperability between different systems and services, allowing for seamless integration and sharing of data.
- Privacy and Security: Web 3.0 will prioritize user privacy and security, with a focus on developing more secure and decentralized systems that protect user data and prevent unauthorized access.
- Internet of Things: Web 3.0 will enable the integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) into the web, with connected devices and sensors providing a wealth of data and new possibilities for innovation.
Web 4.O and Web 5.O
We can dig deeper. Let’s move to Web 4.O and Web 5.O.
 People says, Web 4.O is an intelligent web but Web 5.O will be a telepathic web. Web 5.O is sort of a subsequent addition to what Web 3.O was already offering.
People says, Web 4.O is an intelligent web but Web 5.O will be a telepathic web. Web 5.O is sort of a subsequent addition to what Web 3.O was already offering.
Imagine, if your account would be banned, your digital identity would be vanished. Then from where you can access your information?
You won’t be able to take that out. Web 5.O is being evolved to bit this issue. No control over individual’s data. It is giving you an option of creating an identity which is with you. It is going to be stored in your personal location.
 You will be able to move your specific identity from one platform to the other platform and all the data associated with that particular platform can be transferred to the other platform. In a nutshell, you can use the services seamlessly.
You will be able to move your specific identity from one platform to the other platform and all the data associated with that particular platform can be transferred to the other platform. In a nutshell, you can use the services seamlessly.
Probable Advantages:
- You control your data
- No vendor lock-in
- Your data is with you
- Easy to switch from Service 1 to Service 2
Conclusion
The evolution of the World Wide Web has been nothing short of remarkable. From its humble beginnings as a way for researchers to share information, to its current state as an all-encompassing network of information, communication, and commerce, the web has transformed the way we live our lives.
From the static web to intelligent web, it created new opportunities for education, business, and social interaction, and has brought people together from all corners of the globe.
As we continue to push the boundaries of what is possible on the web, it is clear that its evolution is far from over. With the constant innovation and development of new technologies, the future of the World Wide Web is an exciting and promising one. It is evolving.
Hacking Tools
Explore All Hacking Tools »
UFTP is an encrypted multicast file transfer program for secure, reliable & efficient transfer of files. It also helps in data distribution over a satellite link.
Read DetailsBreaking News
Breaking News Of Each Month »
The recent pandemic was unexpected and unknown to most part of the world. It has changed our life and we are slowly adapting to our new lifestyle. The risks associated with the new lifestyle, both personal & corporate, are unknown to most of us.
Read Details