Aww, clouds spread all around! What…. Will it rain this time?
Oh no! I am not talking about clouds or rain. We are going to discuss such a topic that is in global demand. Hope you have guessed it. Yes, it's all about cloud computing technology. Some of you may or may not have practiced this. Today we shall get a basic comprehensive about this. Here you go!
If I am not mistaken, the first question in your mind now is, what is Cloud Computing?
According to Rajkumar Buyya, "A Cloud is a type of parallel and distributed system consisting of a collection of interconnected and virtualized computers that are dynamically provisioned and presented as one or more unified computing resources based on service-level agreements established through negotiation between the service provider and consumers."
In the simplest term, cloud computing is such a service that is far better than on-premises services. Which makes the difference between these both? Let's understand the Cloud architecture within 2 minutes.
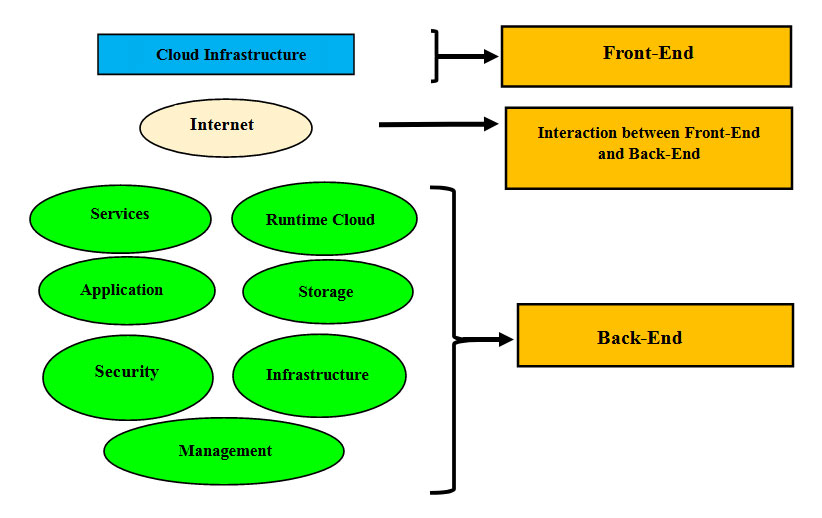
What happens in the Front-End section?
- Managed by client
- Contains all the client-side interfaces and applications that are required to access the cloud platform
What happens in the Back-End section?
- Managed by the service provider
- Maintains all the resources that are required to provide cloud computing services
- Comprises a large amount of data storage, security mechanisms, service models, deployment models, virtualization, and many more
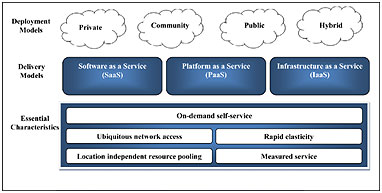
The essential characteristics which have fuelled our thirst for cloud computing are-
Broad Network Access
 Resources' capabilities are available over the network and anybody can access it through standard mechanisms from anywhere, anytime in the world.
Resources' capabilities are available over the network and anybody can access it through standard mechanisms from anywhere, anytime in the world.
Rapid Elasticity
Ability to quickly provision resources as per the need of the individuals. Features of scale in and scale out.
Measured Service
Control and optimize resources by grasping a metering capability at some level of abstraction appropriate to the type of service. Resource usage can be monitored, controlled, and reported. Transparent services are provided for both the provider and consumer of the service.
On-Demand Self-Service
Consumers can directly request and receive access to a service offering without a third party.
Resource Pooling
The provider's computing resources are pooled to serve multiple consumers using a multi-tenant model, with different physical and virtual resources dynamically assigned and reassigned according to consumer demand. A resource can be storage, memory, bandwidth, or a virtual machine.
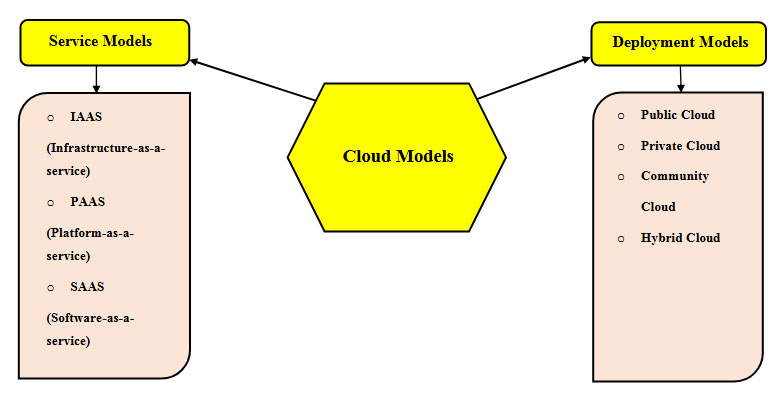
Now we shall know quickly about the cloud service models.
Infrastructure-as-A-Service:
 Maintains computer architecture and resources. Run by the system administrator. The capability provided to the consumer is to provision processing, storage, networks, and other fundamental computing resources.
Maintains computer architecture and resources. Run by the system administrator. The capability provided to the consumer is to provision processing, storage, networks, and other fundamental computing resources.- The consumer can deploy and run arbitrary software, which can include operating systems and applications.
- The user does not manage or control the underlying cloud infrastructure but has control over operating systems, storage, deployed applications, and possibly limited control of select networking components (e.g., host firewalls).
Example – Amazon EC2
What are the Pros and Cons of IAAS?
Pros –
- Readymade infrastructure
- Enhanced scalability
- Flexibility
- Supporting dynamic workloads
Cons –
- Security issues
- Service and network delay
Platform-as-A-Service:
 Run by developers.
Run by developers.- The capability provided to the consumer is to deploy onto the cloud infrastructure consumer-created or acquired applications created using programming languages and tools supported by the provider.
- The consumer does not manage or control the underlying cloud infrastructure including network, servers, operating systems, or storage, but has control over the deployed applications and possibly application hosting environment configurations.
Example – Microsoft Azure, Google App Engine
Do you know its Pros and Cons?
Pros -
- Scalable and cost-effective
- Faster market growth for developers
- Features of Public and Private cloud
- Improvement of web applications
Cons –
- Language barrier
- Migration issues
Software-as-A-Service:
 Run by end customers. The capability provided to the consumer is to use the provider's applications running on a cloud infrastructure.
Run by end customers. The capability provided to the consumer is to use the provider's applications running on a cloud infrastructure.- The applications are accessible from various client devices through a thin client interface such as a web browser (e.g., web-based email).
- The consumer does not manage or control the underlying cloud infrastructure including network, servers, operating systems, storage, or even individual application capabilities, with the possible exception of limited user-specific application configuration settings.
Example – AWS, Salesforce
Know about the Pros and Cons of this particular approach.
Pros –
- Have excellency in team work
- Modest software tools by vendors
- Usage of multi-tenancy model
- Universally accessible from anywhere, anytime
Cons –
- Portability issues
- Browser issues
- Compliance restrictions
Have a keen interest in cloud deployment models?
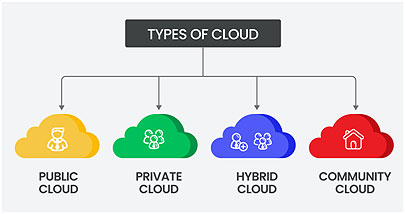
Public Cloud:
The cloud infrastructure is made available to the general public or a large industry group and is owned by an organization selling cloud services.
Examples of Public Cloud:
- Google App Engine
- Microsoft Windows Azure
- IBM Smart Cloud
- Amazon EC2
Private Cloud:
The cloud infrastructure is operated solely for a single organization. It may be managed by the organization or a third party and may exist on-premises or off-premises.
Examples of Private Cloud:
- Eucalyptus
- Ubuntu Enterprise Cloud - UEC
- Amazon VPC (Virtual Private Cloud)
- VMware Cloud Infrastructure Suite
- Microsoft ECI data center
Community Cloud:
The cloud infrastructure is shared by several organizations and supports a specific community that has shared concerns (e.g., mission, security requirements, policy, or compliance considerations). It may be managed by the organizations or a third party and may exist on-premises or off-premises.
Examples of Community Cloud:
- Google Apps for Government
- Microsoft Government Community Cloud
Hybrid Cloud:
The cloud infrastructure is a composition of two or more clouds (private, community, or public) that remain unique entities but are bound together by standardized or proprietary technology that enables data and application portability (e.g., cloud bursting for load-balancing between clouds).
Examples of Hybrid Cloud:
- Windows Azure (capable of Hybrid Cloud)
- VMware vCloud(Hybrid Cloud Services)
Benefits of Cloud Computing
1. Business benefits of Cloud Computing
 Almost zero upfront infrastructure investment
Almost zero upfront infrastructure investment- Just-in-time Infrastructure
- More efficient resource utilization
- Usage-based costing
- Reduced time to market
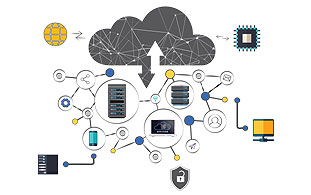
2. Technical benefits of Cloud Computing
 Automation – "Scriptable infrastructure"
Automation – "Scriptable infrastructure"- Auto-scaling
- Proactive Scaling
- More Efficient Development lifecycle
- Improved Testability
- Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
Conclusion
 The most important technology today is Cloud Computing technology. Its demand is increasing rapidly for its driven attributes. Cloud Computing offers better service for half the money a company costs to buy on-premises resources. This modern technology allows you to pay only for how much you use i.e., "Pay-as-you-go".
The most important technology today is Cloud Computing technology. Its demand is increasing rapidly for its driven attributes. Cloud Computing offers better service for half the money a company costs to buy on-premises resources. This modern technology allows you to pay only for how much you use i.e., "Pay-as-you-go".
Nowadays, it turns into a popular practice that involves data security with good backup system not only for a person, but for the world. From individuals to companies and from vendor to buyer, all have migrated to cloud platforms for gaining better security, scalability, storage and mobility.
Hacking Tools
Explore All Hacking Tools »
UFTP is an encrypted multicast file transfer program for secure, reliable & efficient transfer of files. It also helps in data distribution over a satellite link.
Read DetailsBreaking News
Breaking News Of Each Month »
The recent pandemic was unexpected and unknown to most part of the world. It has changed our life and we are slowly adapting to our new lifestyle. The risks associated with the new lifestyle, both personal & corporate, are unknown to most of us.
Read Details