When Hackers Are SMART, Investigators Need To Be SMARTER.
CHFI v11 includes all the essentials of digital forensics analysis and evaluation required for today’s digital world. From identifying the footprints of a breach to collecting evidence for a prosecution, CHFI v11 walks students through every step of the process with experiential learning. This course has been tested and approved by veterans and top practitioners of the cyber forensics industry.
CHFI v11 is engineered by industry practitioners for both professionals and aspiring professionals alike from careers including forensic analysts, cybercrime investigators, cyber defense forensic analysts, incident responders, information technology auditors, malware analysts, security consultants, and chief security officers.
EC-Council’s Certified Hacking Forensic Investigator (CHFI) is the only comprehensive ANSI accredited, lab-focused program in the market that gives organizations vendor-neutral training in digital forensics. CHFI is an ANSI 17024 accredited certification, globally recognized for digital forensic professionals and compliant with international standards. CHFI provides its attendees with a firm grasp of digital forensics, presenting a detailed and methodological approach to digital forensics and evidence analysis that also pivots around Dark Web, IoT, and Cloud Forensics. The program emphasizes proper Chain of Custody procedures, legal admissibility of digital evidence, and preservation techniques aligned with global forensic and compliance standards. The tools and techniques covered in this program will prepare the learner for conducting digital investigations using ground-breaking digital forensics technologies.
The program equips candidates with the necessary skills to proactively investigate complex security threats, allowing them to investigate, record, and report cybercrimes to prevent future attacks.
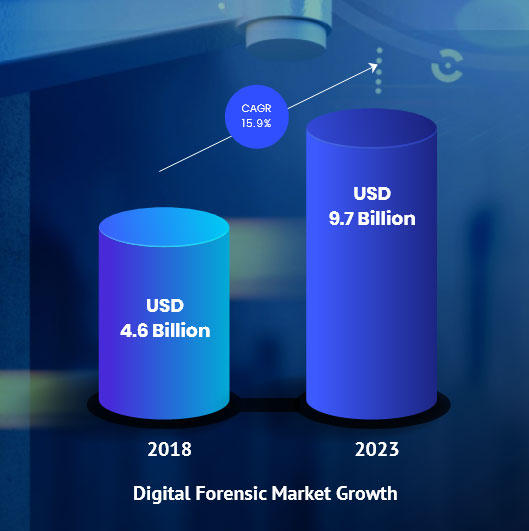
Every crime leaves a digital footprint, and we have the skills to track those footprints. Every crime leaves a digital trail and with EC-Council’s CHFI v11, you will learn to unravel these pieces of evidence, decode them, and report them. From decoding a hack to taking legal action against the perpetrators, you will be an active respondent in times of cyber-breaches. With organizations rapidly adopting new digital technologies and cyberattacks being a prime risk factor, it is no surprise that computer forensics is the need of the hour. The estimated growth of the worldwide forensics market is projected at USD 9.7 billion.
Why learn CHFI v11 - Computer Hacking Forensic Investigator?
Certified Hacking Forensic Investigator v10 has been designed by industry experts to provide an unbiased approach to applying complex investigation practices, empowering Forensic Professionals to:
Play an active role in
investigating and preserving digital and non-digital evidence
of an attack.
Counter to the
series of compromises.
Use
threat intelligence to anticipate and alert
cyber teams in case of future attacks.
A BREACH can be BRUTAL. Investing in building an expert in-house forensics team with CHFI training and certification is a strategic move for enterprises looking to safeguard their stakeholders’ interests as well as their own. CHFI empowers their existing team with learning the latest investigation practices.
- The course aligns with all the crucial forensic job roles across the globe.
- It is an ANSI 17024 accredited Certification Program, mapped to the NICE 2.0 framework.
- The course focuses on the latest technologies including IoT Forensics, Dark Web Forensics, Cloud Forensics (including Azure and AWS), Network Forensics, Database Forensics, Mobile Forensics, Malware Forensics (including Emotet and Eternal Blue), OS Forensics, RAM forensics and Tor Forensics, CHFI v11 covers the latest tools, techniques, and methodologies along with ample crafted evidence files.
- EC-Council is one of the few ANSI 17024 accredited institutions globally that specializes in Information Security.
- The Computer Hacking Forensic Investigator (CHFI) credential is an ANSI 17024 accredited certification.
- The CHFI v11 program has been redesigned and updated after a thorough investigation into current market requirements, job tasks analysis, and the recent industry focus on forensic skills.
- It is designed and developed by experienced subject matter experts and digital forensics practitioners.
- CHFI v11 program includes extensive coverage of Malware Forensics processes, along with new modules such as Dark Web Forensics and IoT Forensics.
- It also covers detailed forensic methodologies for public cloud infrastructure, including Amazon AWS and Azure.
- The program is developed with an in-depth focus on Volatile data acquisition and examination processes (RAM Forensics, Tor Forensics, etc.).
- CHFI v11 is a complete vendor-neutral course covering all major forensics investigation technologies and solutions.
- CHFI has detailed labs for a hands-on learning experience. On average, 50% of training time is dedicated to labs, loaded on EC-Council’s CyberQ (Cyber Ranges).
- It covers all the relevant knowledge bases and skills to meet regulatory compliance standards such as ISO 27001, PCI DSS, SOX, HIPPA, etc.
- It comes with an extensive number of white papers for additional reading.
- The program presents a repeatable forensics investigation methodology from a versatile digital forensic professional, increasing employability.
- The courseware is packed with forensics investigation templates for evidence collection, the chain of custody, final investigation reports, etc.
- The program comes with cloud-based virtual labs, loaded on advanced Cyber Ranges, enabling students to practice various investigation techniques in real-time and realistically simulated environments.
Industries that Prefer CHFI Professionals

With Our Years of Expertise and Experience, comes CHFI v11
ANSI 17024 accredited Certification Program | Mapped to the NICE 2.0 framework | Recognized by the DoD under Directive 8570
- Includes critical modules in Dark Web Forensics and IoT Forensics
- More than 68% of new and advanced forensic lab
- Extensive coverage of Malware Forensics (latest malware samples such as Emotet and EternalBlue)
- Latest forensic tools including Splunk, DNSQuerySniffer, etc.
- Significant coverage of forensic methodologies for public cloud infrastructure, including Amazon AWS and Microsoft Azure
- In-depth focus on Volatile and Non-volatile data acquisition and examination process (RAM Forensics, Tor Forensics, etc.)
- More than 70GB of crafted evidence files for investigation purposes
- New techniques such as Defeating Anti-forensic technique, Windows ShellBags including analyzing LNK files and Jump Lists
- Massive updates on all modules in CHFI
Course Outline
Duration
40 hours - 2 classes per week
Eligibility
Basic knowledge of Hardware, Software & Network. Prior completion of CEH training would be an advantage.
Course Fees
Class Room Training
Rs.47,999/-
Inclusive of all taxes
Online Training
Rs.57,999/-Rs.47,999/-
Inclusive of all taxes
What You Will Get?
40 Hours
of in depth training in lab environment by the EC Council certified instructors and best cyber security and computer forensic experts
Study Materials
Voucher code from EC Council, Tools and Software
CHFI v11
Certificate of Completion after examination and alumni status
Important Notice for International Students: The EC-Council global course fee and Exam Voucher fee will depend on the candidate's location and foreign currency exchange rate.
Course Benefits:
Detailed Methodological Learning Approach
CHFI presents a methodological approach to computer forensic including searching and seizing, chain-of-custody, acquisition, preservation, analysis and reporting of digital evidence.
Dark Web & IoT Forensics
The first certification program to offer you Dark Web and IoT Forensics modules.
Extensive Coverage on Malware Forensics
Covers latest malware samples like Emotet and Eternal Blue, also known as WannaCry.
Forensic Methodologies for Cloud Infrastructure
Master tools and techniques to ensure security across various cloud platforms — Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure Cloud, and Google Cloud Platform.
70+ GB of Crafted Evidence Files
CHFI v11 provides you with 70 GB of crafted evidence files for investigation purposes which helps to have hands-on experience in evidence collection.
68+ Complex Labs
The only program that provides thorough learning with a simulated environment with 68+ complex labs to ensure you obtain must have skills for your next job.
Lab Manual & Student Manual (will be added)
The CHFI program provides 2,100+ pages of official EC-Council curriculum content and 1,550+ pages of structured lab exercises, ensuring comprehensive conceptual understanding and real-world practical exposure.
Digital Forensics Tools (will be added)
Training includes access to 600+ advanced digital forensic tools for practical investigation skills.
Your Course Path
Course Details
- The duration of the course is 40 hours - 2 Classes per week
- The course fee is Rs.47,999/- Inclusive of all taxes (Classroom Training) & Rs.57,999/- Rs.47,999/- Inclusive of all taxes (Online Training)
- The course is taught in theory as well as practical
- The course is designed and developed for digital forensic practitioners
- A complete computer/digital forensic investigation technologies and solutions guide
- Detailed labs for hands-on learning experience
- Covers all the relevant knowledge-bases and skills to meets government and corporate standards
- The program presents a repeatable forensic investigation methodology required from a versatile digital forensic professional which increases your employability
About the Exam
The CHFI certification is awarded after successfully passing exam EC0 312-49. CHFI EC0 312-49 exams are available at ECC exam centers around the world.
CHFI Exam Details
- Number of Questions: 150
- Test Duration: 4 hours
- Test Format: Multiple Choice
- Test Delivery: ECC exam portal
Passing Score
In order to maintain the high integrity of our certification exams, EC-Council Exams are provided in multiple forms (i.e., different question banks). Each form is carefully analyzed through beta testing with an appropriate sample group under the purview of a committee of subject matter experts, ensuring that each of our exams is not only academically sound, but also has "real world" applicability. We apply an internal process to determine the difficulty rating of each question. The individual rating then contributes to an overall "Cut Score" for each exam form. To ensure each form has equal assessment standards, cut scores are set on a "per exam form" basis. Depending on which exam form is challenged, cut scores can range from 60% to 85%.
Hacking Tutorials
Read All Tutorials »
Building a career in Digital Forensics - How promising is the future? A thorough career guide
Read Details »Hacking Videos
Explore All Videos »How to Hiding Your Secret File using Steganography?
View On Youtube »Enroll Now
Fields marked with * are mandatory.
Ratings & Reviews
How CHFI Transformed Careers: Success Stories of Cyber Security Professionals
Valued by Leading Organizations Across the World

Job Prospects & Job Sources
The various positions in which a CHFI expert can apply for are,
| IT Security Specialist | Network Security Pro | Penetration Tester |
| IT Auditor Positions | Security Engineer | Cyber Forensics Analyst |
| Forensic Analyst - Incident Response | Digital Forensic Investigator |
As organizations try hard to combat cyber attacks, businesses and government agencies are increasingly employing top-notch expertise for important information security jobs. Computer forensics investigation – the detection and analysis of cyber crime evidence for legal proceedings and precaution is one of the most crucial and promising IT security jobs in that respect.
Workforce demand for Computer Hacking Forensic Investigators is on an all time high across multiple work options; major industries for CHFI hiring include law enforcement, military and defence, enterprise IT, insurance and banking, legal practices, and of course cyber security firms.
The pay packet for CHFI experts in India on an average is Rs.21 lakhs.
FAQs
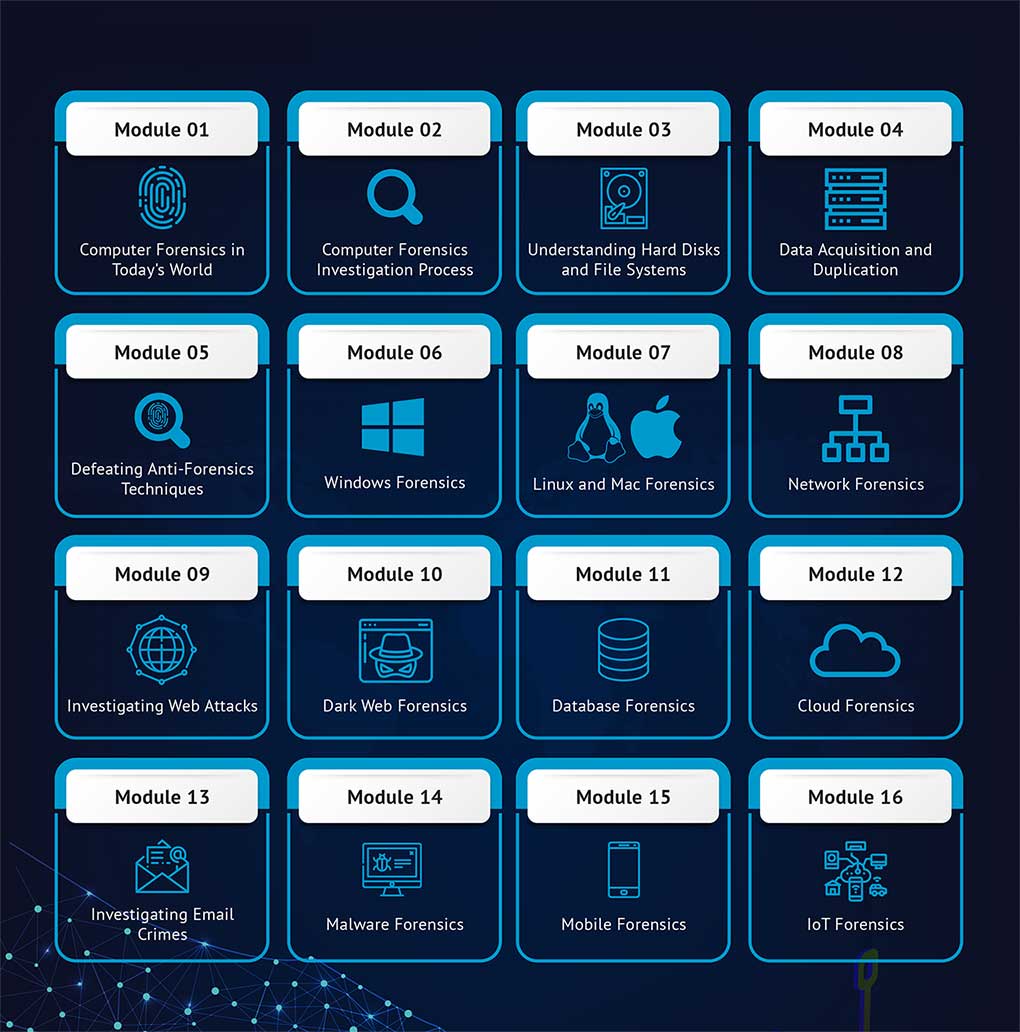
- Module 01: Computer Forensics in Today’s World
- Module 02: Computer Forensics Investigation Process
- Module 03: Understanding Hard Disks and File Systems
- Module 04: Data Acquisition and Duplication
- Module 05: Defeating Anti-Forensics Techniques
- Module 06: Windows Forensics
- Module 07: Linux and Mac Forensics
- Module 08: Network Forensics
- Module 09: Investigating Web Attacks
- Module 10: Dark Web Forensics
- Module 11: Database Forensics
- Module 12: Cloud Forensics
- Module 13: Investigating Email Crimes
- Module 14: Malware Forensics
- Module 15: Mobile Forensics
- Module 16: IoT Forensics
The duration of the course is 40 hours - 2 classes per week.
The course is taught in theory as well as practical.
The prerequisites of the course are Basic knowledge of Hardware, Software & Network.
Workforce demand for Computer Hacking Forensic Investigators is on an all time high across multiple work options; major industries for CHFI hiring include law enforcement, military and defence, enterprise IT, insurance and banking, legal practices, and of course cyber security firms..
You can apply for corporate designation after this.
Course Fees
Rs.57,999/-Rs.47,999/-
Inclusive of all taxes
Batches
Weekend Batches for Kolkata Center:
Mar, 2026
Mar, 2026
May, 2026
Weekday Batches for Siliguri Center:
Mar, 2026
Mar, 2026
May, 2026
Member of: